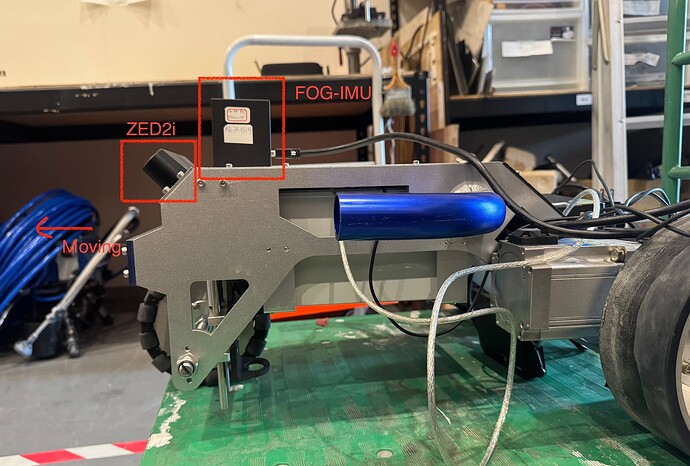
To improve pose accuracy and reduce drift during rotation, I’m trying to replace the ZED2i’s built-in IMU with my own FOG-IMU (Fiber-Optic Gyroscope). I’m using ROS 2 (Humble) and the robot_localization package for sensor fusion with an Extended Kalman Filter (EKF). Here’s what I did:
- Set
imu_fusiontofalseincommon_stereo.yaml. - Launched ZED node with:
ros2 launch zed_wrapper zed_camera.launch.py camera_model:=zed2i - Created a custom ROS2 node to publish my FOG-IMU data at
/Fog_imu/imu_data. - Launched EKF fusion node:
ros2 launch ekf_fusion.launch.py
# ekf_fusion.launch.py
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch_ros.actions import Node
def generate_launch_description():
return LaunchDescription([
# Static transform: imu_link → base_link
Node(
package='tf2_ros',
executable='static_transform_publisher',
name='imu_to_base',
arguments=['0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', 'base_link', 'imu_link'],
),
# EKF node
Node(
package='robot_localization',
executable='ekf_node',
name='ekf_filter',
output='screen',
parameters=[{
'use_sim_time': False,
'frequency': 50.0,
'sensor_timeout': 0.1,
'two_d_mode': False,
'publish_tf': True,
'transform_tolerance': 0.1,
'pose0': '/zed/zed_node/pose_with_covariance',
'pose0_config': [
True, True, True, # X, Y, Z
False, False, False, # roll, pitch, yaw
False, False, False, # VX, VY, VZ
False, False, False, # VRoll, VPitch, VYaw
False, False, False, # AX, AY, AZ
],
'pose0_differential': False,
'pose0_queue_size': 5,
'imu0': '/Fog_imu/imu_data',
'imu0_config': [
False, False, False, # X, Y, Z
True, True, True, # roll, pitch, yaw
False, False, False, # VX, VY, VZ
True, True, True, # VRoll, VPitch, VYaw
False, False, False, # AX, AY, AZ
],
'imu0_differential': False,
'imu0_queue_size': 5,
'odom0': '/zed/zed_node/odom',
'odom0_config': [
False, False, False,
False, False, False,
False, False, False,
False, False, False,
False, False, False
],
'odom0_differential': False,
'odom0_queue_size': 10
}]
)
])
- Monitored the output from
/odometry/filtered.
Platform Specs:
- Jetson Orin NX 8GB
- ROS 2: Humble
- ZED SDK: 5.0.1 (L4T 36.4)
 Problem Encountered
Problem Encountered
I noticed that:
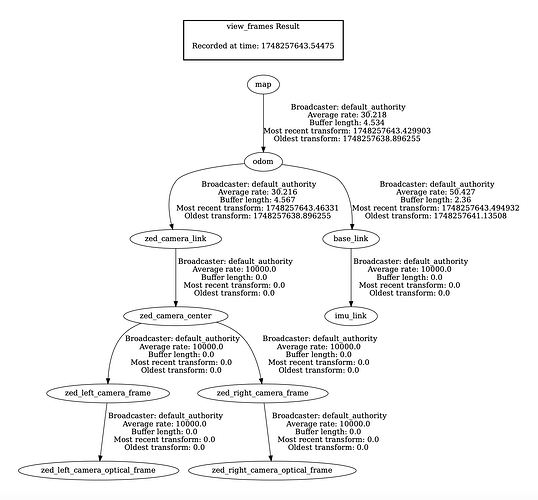
/zed/zed_node/pose_with_covariancehasframe_id = "map"/odometry/filteredhasframe_id = "odom"
As a result, /odometry/filtered outputs nearly identical values to /zed/zed_node/odom, which is not what I expected.
To address this, I duplicated the topic /zed/zed_node/pose_with_covariance into a new one /zed/zed_node/pose_cov_for_ekf, but changed the frame_id to "odom". Feeding this to the EKF seems to work: the /odometry/filtered position aligns more closely with the corrected /pose.
However, as a ROS beginner, I’m unsure whether this is the correct approach. Should I have instead set world_frame = "map" in robot_localization and kept the original topic? What is the recommended way to handle this kind of frame inconsistency?
 Additional Context
Additional Context
Due to the hardware configuration, the ZED2i is mounted at a 45° upward angle relative to the mobile robot. When the robot moves forward, the /zed/zed_node/odom Z-position drifts negatively (goes downward), which is incorrect. But the /zed/zed_node/pose output stays aligned with the true vertical axis. This is likely due to set_gravity_as_origin = true, which uses IMU gravity information to keep the orientation aligned with the real-world Z-axis.