Hello,
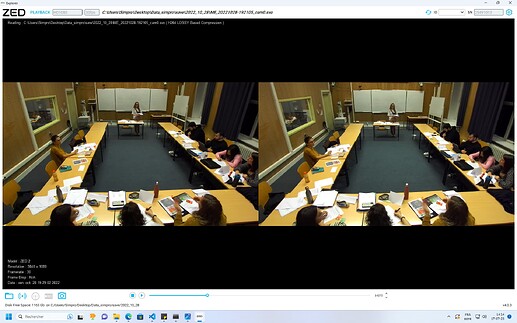
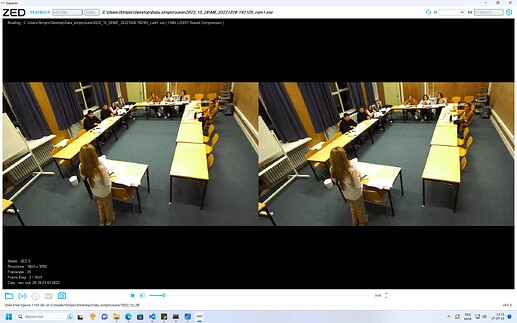
I’m currently working on the fused_camera for body tracking and I’m extracting a lot of information from the various skeletons in order to use them and analyze behavior.
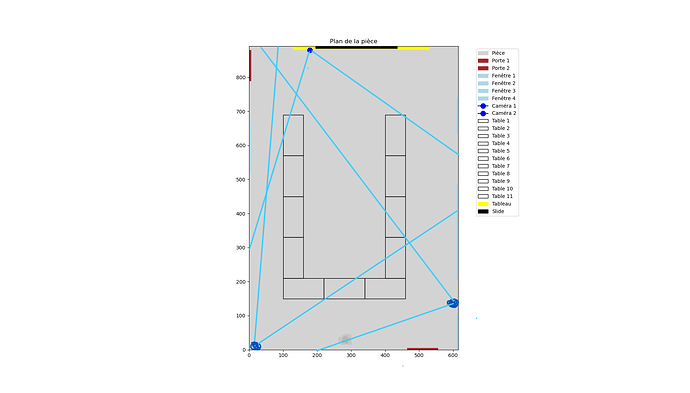
However, there’s a big problem re-identifying skeletons when they’re visible, then they’re not, then they become visible again (when they appear and disappear).
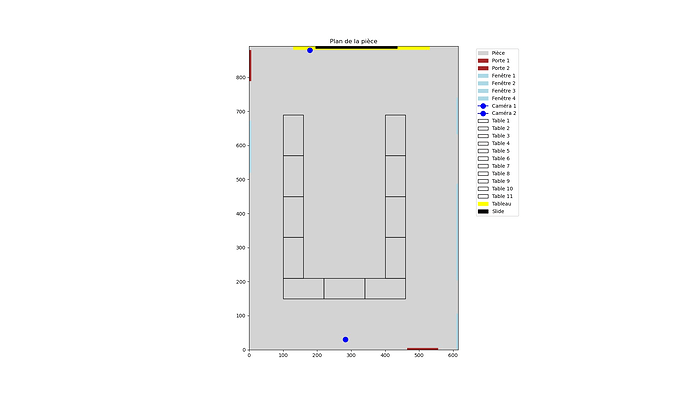
If I take my example in which I analyze a 50min svo file, there are basically 8 people, and I obtain, after analysis, a json file containing the information I collect for over 300 different IDs…
Is there a solution? Is it possible that I haven’t activated a necessary parameter?
Here’s my code:
############################################################################
'''
Ce code prend en entrée le fichier de calibration des caméras et permet de :
- détecter et visualiser le squelette fusionné dans le viewer de Stereolabs
- enregistrer un grand nombre de données des squelettes fusionnés à chaque
timestamps (position, bounding box, keypoints, ...)
- visualiser en temps réel la position actuelle du squelette (poit rouge)
ainsi que ses précédentes (trajectoire bleu)
- visualiser en temps réel la Heatmap basée sur la position du squelette
'''
############################################################################
import cv2
import sys
import pyzed.sl as sl
import time
import ogl_viewer.viewer as gl
import numpy as np
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from tkinter import Tk
from tkinter.filedialog import askopenfilename
import os
#######################################################################
#
# Choisir de travailler à partir du flux vidéo ou de fichiers .svo
#
#######################################################################
def get_file_path():
Tk().withdraw()
file_path = askopenfilename()
return file_path
def display_menu():
print(" ")
print("Choose 1 or 2 :")
print("1. Work with 2 svo file")
print("2. Work with live stream of cameras")
print(" ")
def get_user_choice():
while True:
choice = input("Enter option 1 or 2 : ")
if choice in ['1', '2']:
return choice
else:
print("Invalid Option. Please, retry.")
def zed360_file_adapt_to_work_with_svo(filepath):
svo_paths = {
"25491013": "path/to/file.svo",
"27490510": "path/to/file.svo"
}
# Charger le premier fichier JSON
with open(filepath, 'r') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
# Mettre à jour les chemins d'accès dans le fichier JSON
for key, value in svo_paths.items():
data[key]["input"]["zed"]["configuration"] = value
data[key]["input"]["zed"]["type"] = "SVO_FILE"
# Enregistrer les modifications dans le deuxième fichier JSON
with open('svo_cali.json', 'w') as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4)
# Obtenir le chemin absolu du répertoire courant
current_directory = os.getcwd()
# Concaténer le nom du fichier pour obtenir le filepath complet
filepath_svo = os.path.join(current_directory, "svo_cali.json")
return filepath_svo
def select_live_or_svo(filepath):
# Afficher le menu
display_menu()
# Récupérer le choix de l'utilisateur
user_choice = get_user_choice()
# Utiliser le choix de l'utilisateur
if user_choice == '1':
print("You choose option 1 : Work with 2 svo file")
print(" ")
print("Select the svo files (cam0 and then cam1) corresponding to the recording to be processed")
print(" ")
filepath_svo = zed360_file_adapt_to_work_with_svo(filepath)
# Chargement du fichier JSON
with open(filepath_svo, 'r') as json_file:
data = json.load(json_file)
# Modification des chemins d'accès dans le fichier JSON
filepath1 = data["25491013"]["input"]["zed"]["configuration"] = get_file_path()
print("You choose to work with :")
print("- File 1 : ", filepath1)
filepath2 = data["27490510"]["input"]["zed"]["configuration"] = get_file_path()
#print("and")
print("- File 2 : ", filepath2)
file_name_with_extension = os.path.basename(filepath1)
file_name_without_extension = os.path.splitext(file_name_with_extension)[0]
new_filename = "Calibration_file_for_" + file_name_without_extension + "_1"
# Extraire le répertoire du fichier
directory = os.path.dirname(filepath)
# Construire le nouveau chemin d'accès avec le nouveau nom de fichier
new_filepath = os.path.join(directory, f"{new_filename}.json")
print(" ")
print("New calibration file name : ", new_filepath)
print(" ")
# Enregistrement des modifications dans le fichier JSON
with open(new_filepath, 'w') as json_file:
json.dump(data, json_file, indent=4)
# Supprimer le fichier svo intermédiare qui a été créé
if os.path.exists(filepath_svo):
os.remove(filepath_svo)
filepath = new_filepath
if user_choice == '2':
print("You choose option 2 : Work with live stream of cameras")
filepath = sys.argv[1]
return filepath
#######################################################################
#
# Fonctions permettant l'enregistrement de l'ensemble des données des
# squelettes dans un fichier .json
#
#######################################################################
def addIntoOutput(out, identifier, tab):
out[identifier] = []
for element in tab:
out[identifier].append(element)
return out
def serializeBodyData(body_data):
"""Serialize BodyData into a JSON like structure"""
out = {}
out["id"] = body_data.id
out["unique_object_id"] = str(body_data.unique_object_id)
out["tracking_state"] = str(body_data.tracking_state)
out["action_state"] = str(body_data.action_state)
addIntoOutput(out, "position", body_data.position)
#addIntoOutput(out, "velocity", body_data.velocity)
#addIntoOutput(out, "bounding_box_2d", body_data.bounding_box_2d)
out["confidence"] = body_data.confidence
#addIntoOutput(out, "bounding_box", body_data.bounding_box)
addIntoOutput(out, "dimensions", body_data.dimensions)
addIntoOutput(out, "keypoint_2d", body_data.keypoint_2d)
addIntoOutput(out, "keypoint", body_data.keypoint)
#addIntoOutput(out, "keypoint_cov", body_data.keypoints_covariance)
#addIntoOutput(out, "head_bounding_box_2d", body_data.head_bounding_box_2d)
#addIntoOutput(out, "head_bounding_box", body_data.head_bounding_box)
addIntoOutput(out, "head_position", body_data.head_position)
addIntoOutput(out, "keypoint_confidence", body_data.keypoint_confidence)
#addIntoOutput(out, "local_position_per_joint", body_data.local_position_per_joint)
#addIntoOutput(out, "local_orientation_per_joint", body_data.local_orientation_per_joint)
#addIntoOutput(out, "global_root_orientation", body_data.global_root_orientation)
#print(dir(body_data))
return out
def serializeBodies(bodies):
"""Serialize Bodies objects into a JSON like structure"""
out = {}
out["is_new"] = bodies.is_new
out["is_tracked"] = bodies.is_tracked
out["timestamp"] = bodies.timestamp.data_ns
out["body_list"] = []
for sk in bodies.body_list:
out["body_list"].append(serializeBodyData(sk))
return out
class NumpyEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):
def default(self, obj):
if isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
return obj.tolist()
return json.JSONEncoder.default(self, obj)
#######################################################################
#
# MAIN
#
#######################################################################
if __name__ == "__main__":
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("This sample display the fused body tracking of multiple cameras.")
print("It needs a Localization file in input. Generate it with ZED 360.")
print("The cameras can either be plugged to your devices, or already running on the local network.")
exit(1)
filepath = sys.argv[1]
filepath = select_live_or_svo(filepath)
fusion_configurations = sl.read_fusion_configuration_file(filepath, sl.COORDINATE_SYSTEM.RIGHT_HANDED_Y_UP, sl.UNIT.METER)
if len(fusion_configurations) <= 0:
print("Invalid file.")
exit(1)
senders = {}
network_senders = {}
# common parameters
init_params = sl.InitParameters()
init_params.coordinate_system = sl.COORDINATE_SYSTEM.RIGHT_HANDED_Y_UP
init_params.coordinate_units = sl.UNIT.METER
init_params.depth_mode = sl.DEPTH_MODE.ULTRA
init_params.camera_resolution = sl.RESOLUTION.HD720
communication_parameters = sl.CommunicationParameters()
communication_parameters.set_for_shared_memory()
positional_tracking_parameters = sl.PositionalTrackingParameters()
positional_tracking_parameters.set_as_static = True
body_tracking_parameters = sl.BodyTrackingParameters()
body_tracking_parameters.detection_model = sl.BODY_TRACKING_MODEL.HUMAN_BODY_ACCURATE
body_tracking_parameters.body_format = sl.BODY_FORMAT.BODY_18
body_tracking_parameters.enable_body_fitting = False
body_tracking_parameters.enable_tracking = True
for conf in fusion_configurations:
print("Try to open ZED", conf.serial_number)
init_params.input = sl.InputType()
# network cameras are already running, or so they should
if conf.communication_parameters.comm_type == sl.COMM_TYPE.LOCAL_NETWORK:
network_senders[conf.serial_number] = conf.serial_number
# local camera needs to be run form here, in the same process than the fusion
else:
init_params.input = conf.input_type
senders[conf.serial_number] = sl.Camera()
init_params.set_from_serial_number(conf.serial_number)
status = senders[conf.serial_number].open(init_params)
if status != sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
print("Error opening the camera", conf.serial_number, status)
del senders[conf.serial_number]
continue
status = senders[conf.serial_number].enable_positional_tracking(positional_tracking_parameters)
if status != sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
print("Error enabling the positional tracking of camera", conf.serial_number)
del senders[conf.serial_number]
continue
status = senders[conf.serial_number].enable_body_tracking(body_tracking_parameters)
if status != sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
print("Error enabling the body tracking of camera", conf.serial_number)
del senders[conf.serial_number]
continue
senders[conf.serial_number].start_publishing(communication_parameters)
print("Camera", conf.serial_number, "is open")
if len(senders) + len(network_senders) < 1:
print("No enough cameras")
exit(1)
print("Senders started, running the fusion...")
init_fusion_parameters = sl.InitFusionParameters()
init_fusion_parameters.coordinate_system = sl.COORDINATE_SYSTEM.RIGHT_HANDED_Y_UP
init_fusion_parameters.coordinate_units = sl.UNIT.METER
init_fusion_parameters.output_performance_metrics = False
init_fusion_parameters.verbose = True
communication_parameters = sl.CommunicationParameters()
fusion = sl.Fusion()
camera_identifiers = []
fusion.init(init_fusion_parameters)
print("Cameras in this configuration : ", len(fusion_configurations))
# warmup
bodies = sl.Bodies()
for serial in senders:
zed = senders[serial]
if zed.grab() == sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
zed.retrieve_bodies(bodies)
# print(bodies)
for i in range(0, len(fusion_configurations)):
conf = fusion_configurations[i]
uuid = sl.CameraIdentifier()
uuid.serial_number = conf.serial_number
print("Subscribing to", conf.serial_number, conf.communication_parameters.comm_type)
status = fusion.subscribe(uuid, conf.communication_parameters, conf.pose)
if status != sl.FUSION_ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
print("Unable to subscribe to", uuid.serial_number, status)
else:
camera_identifiers.append(uuid)
print("Subscribed.")
if len(camera_identifiers) <= 0:
print("No camera connected.")
exit(1)
body_tracking_fusion_params = sl.BodyTrackingFusionParameters()
body_tracking_fusion_params.enable_tracking = True
body_tracking_fusion_params.enable_body_fitting = False
fusion.enable_body_tracking(body_tracking_fusion_params)
rt = sl.BodyTrackingFusionRuntimeParameters()
rt.skeleton_minimum_allowed_keypoints = 7
viewer = gl.GLViewer()
viewer.init()
# Create ZED objects filled in the main loop
bodies = sl.Bodies()
single_bodies = [sl.Bodies]
# Dimensions de la pièce (à adapter selon votre cas)
ROOM_WIDTH = 10 # Largeur de la pièce en mètres
ROOM_HEIGHT = 10 # Hauteur de la pièce en mètres
# Résolution de la carte de chaleur
HEATMAP_RESOLUTION = 50 # Nombre de points en x et y pour la carte de chaleur
# Initialiser la carte de chaleur
heatmap_data = np.zeros((HEATMAP_RESOLUTION, HEATMAP_RESOLUTION))
# Positions précédentes pour la trajectoire
previous_positions = []
positions = []
# Initialiser le visualiseur
create_visualization()
skeleton_file_data = {}
while (viewer.is_available()):
for serial in senders:
zed = senders[serial]
if zed.grab() == sl.ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
zed.retrieve_bodies(bodies)
if fusion.process() == sl.FUSION_ERROR_CODE.SUCCESS:
# Retrieve detected objects
fusion.retrieve_bodies(bodies, rt)
# for debug, you can retrieve the data send by each camera, as well as communication and process stat just to make sure everything is okay
# for cam in camera_identifiers:
# fusion.retrieveBodies(single_bodies, rt, cam);
'''if bodies.is_new:
body_array = bodies.body_list
print(str(len(body_array)) + " Person(s) detected\n")'''
# enregistrement des données du squelette en fichier json
skeleton_file_data[str(bodies.timestamp.get_milliseconds())] = serializeBodies(bodies)
# permet de voir le squelette dans le viewer
viewer.update_bodies(bodies)
file_sk = open("bodies.json", 'w')
file_sk.write(json.dumps(skeleton_file_data, cls=NumpyEncoder, indent=4))
file_sk.close()
for sender in senders:
senders[sender].close()
viewer.exit()
plt.close('all')